
When venturing into the world of trading, one of the most crucial concepts you’ll encounter is the stop-loss order, often abbreviated as SL. It’s a tool designed to help traders manage risk and protect their investments from significant losses. But what exactly is SL in trading, and how can you effectively use it to safeguard your trades? Let’s dive in and explore everything you need to know about stop-loss orders.
| ⮕ Get the 7 Hidden Forex Secrets—Free PDF Download |
Basics of SL in Trading
Stop-loss (SL) is a predetermined price level at which a trader will exit a trade to prevent further losses. Think of it as a financial safety net that helps you avoid losing more money than you can afford. When the market price hits your SL, your trading platform will automatically sell the asset, thereby limiting your loss.
Why is SL Important in Trading?
The primary purpose of a stop-loss order is to manage risk. Trading, by nature, involves a significant amount of uncertainty. Market conditions can change rapidly, and prices can move against you in a blink. By setting a stop-loss order, you ensure that you won’t lose more than a specified amount, allowing you to stay in the game longer and trade another day.
Types of Stop-Loss Orders
There are several types of stop-loss orders you can use, each with its own advantages and use cases:
Fixed Stop-Loss: This is the simplest form, where you set a fixed price at which your trade will be closed. For example, if you buy a stock at $100 and set a stop-loss at $90, your position will be sold if the price drops to $90.
Trailing Stop-Loss: A trailing stop-loss moves with the price of the asset. If the asset price increases, the SL moves up, but if the asset price decreases, the SL remains the same. This helps you lock in profits while still protecting against a downside move.
Percentage Stop-Loss: Instead of setting a specific price, you set a percentage drop at which the SL will trigger. For example, you might decide to sell if the price drops by 10% from the purchase price.
| ⮕ Get the 7 Hidden Forex Secrets—Free PDF Download |
How to Set a Stop-Loss Order
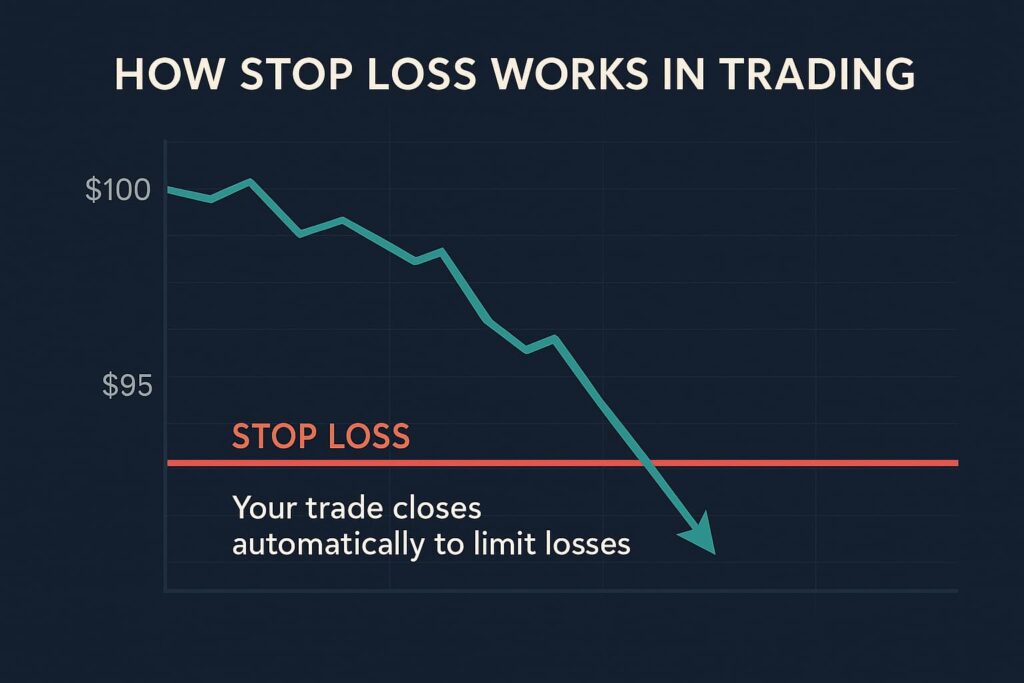
Setting a stop-loss order is straightforward. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Determine Your Risk Tolerance: Decide how much of your capital you’re willing to risk on a single trade. This is typically a percentage of your trading account, often around 1-2%.
- Identify the SL Level: Based on your risk tolerance, calculate the price level at which you want to set your SL. For instance, if you’re willing to risk 2% on a stock bought at $100, your SL would be at $98.
- Place the Order: On your trading platform, place a stop-loss order at the identified level. Ensure that you double-check the details before confirming.
Strategies for Effective SL Use
While setting a stop-loss order is relatively simple, using it effectively requires a bit more strategy. Here are some tips:
Avoid Emotional Trading: One of the biggest benefits of SL is that it takes emotion out of the equation. Stick to your predetermined SL levels and resist the temptation to move them based on gut feelings.
Use Technical Analysis: Technical indicators can help you determine optimal SL levels. Look for support and resistance levels, moving averages, and other key technical markers.
Review and Adjust: Markets change, and so should your SL levels. Regularly review and adjust your SL orders based on market conditions and your trading strategy.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Setting a stop-loss order is an essential skill, but there are some common mistakes that traders make:
Setting SL Too Tight: If your SL is too close to your entry price, you might get stopped by normal market fluctuations. Give your trades some room to breathe.
Ignoring Volatility: Different assets have different levels of volatility. A one-size-fits-all approach to SL levels doesn’t work. Adjust your SL based on the volatility of the asset you’re trading.
Not Using SL at All: Some traders believe they can manually manage their trades and avoid using SL. This can lead to significant losses, especially during rapid market movements.
The Psychological Aspect of Using SL
Beyond the technicalities, using stop-loss orders involves a significant psychological component. Accepting a loss, even a controlled one, can be tough. However, successful trading requires discipline and the ability to stick to your trading plan, including your SL strategy.
| ⮕ Get the 7 Hidden Forex Secrets—Free PDF Download |
SL in Different Markets
Stop-loss orders are not limited to stock trading. They are equally useful in other markets, such as forex, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. Each market has its dynamics, but the fundamental principle of protecting your capital remains the same.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples
To illustrate the importance of stop-loss orders, let’s look at a couple of real-world examples:
Stock Market: Imagine you bought shares of a company at $50, expecting the price to rise. However, due to unexpected bad news, the stock price starts to plummet. If you had set a stop-loss at $45, your position would have been sold automatically, limiting your loss to $5 per share. Without an SL, you might have held on, hoping for a rebound, which might never come.
Forex Market: In forex trading, currency pairs can be extremely volatile. Suppose you entered a long position on the EUR/USD pair at 1.2000. If you set a stop-loss at 1.1950, your loss would be limited to 50 pips if the price moves against you.
| ⮕ Get the 7 Hidden Forex Secrets—Free PDF Download |
FAQs
What is SL in trading?
SL, or stop-loss, is a tool used by traders to limit potential losses by automatically selling an asset when its price reaches a predetermined level.
How do I determine the right SL level?
Your SL level should be based on your risk tolerance, trading strategy, and market conditions. Technical analysis can help you identify optimal SL levels.
Can I adjust my SL after placing it?
Yes, you can adjust your SL based on market conditions and changes in your trading strategy. However, avoid making changes based on emotions.
Is it possible to trade without using SL?
While some traders prefer not to use SL, it is generally not recommended, as it increases the risk of significant losses.
What is the difference between a fixed and a trailing SL?
A fixed SL remains at the same price level, while a trailing SL moves with the price of the asset, helping to lock in profits as the price rises.
How does volatility affect SL?
Higher volatility means larger price swings, so you might need to set a wider SL to avoid being stopped out by normal market fluctuations.
Conclusion
Understanding what SL is in trading is fundamental to managing risk and protecting your investments. Whether you’re a novice trader or an experienced one, using stop-loss orders can help you trade more confidently and effectively. By setting appropriate SL levels and adhering to them, you can mitigate losses and stay on track towards achieving your trading goals. Remember, the key to successful trading is not just making profits but also protecting yourself from significant losses.
